Identification of users for access to on-line sites and services can take a number of guises. Here, we are focussed on claims or attribute-based identities.
These identities are, primarily, groups of claims or attributes of the individual, such as their name or email address, and it is these claims that can be used to identify each user and grant permissions to access to services.
Such identities are much more than simple login authentication systems, unlike those based on a single property such as password based systems, possession of a private key, smartcard or biometric property, as they have the potential to:
- Provide universal, open standards-based user identity data.
- Afford an enhanced user experience, by providing user information required for common registration or access control tasks, such as date of birth.
- Nothing for the user to download, install or maintain.
- Prevent fraudulent applications for services through on-line applications.
- Provide for secure transactions at sites, without requiring users to provide card details to untrusted third parties.
- Provide the end user with full control over the information to be released to sites and services.
- Enhance user privacy
- Enhance security, through elimination of passwords as well as avoiding phishing attacks.
- Provide a consistent user interface for users to identify themselves.
- Make use of users' existing social network data and logins.
- Easily integrated into new or existing sites.
How it works
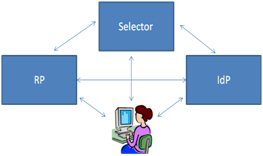
Once an individual is registered with an Identity Provider (IdP), they may access sites and services as follows:
The site (known as a Relying party or RP) requests the user's identity either directly or indirectly from the IdP. As part of this request, the RP specifies the claims or attributes that are required.
This request can pass to an Identity Selector - a system that enables the user to choose one identity from his or her identities, or go directly to the IdP.
In either case, the user will be required to provide authentication in order to access their identity. Once authenticated, the user can authorise the claims data to be returned to the RP, to be processed and used to control access to the site, etc.